So, what is an e-bike? Essentially, it is a bicycle that will give you an extra boost when you pedal. The boost comes from an electric motor powered by a battery.
My team and I love how electric bikes have made our commuting much easier and effortless. We encourage you to read on and learn about this fantastic transportation method.
You will get as excited as we are and consider going bike-electric.
Here are a few things you will learn:
Table of Contents
What is the difference between an e-bike and a normal bike?
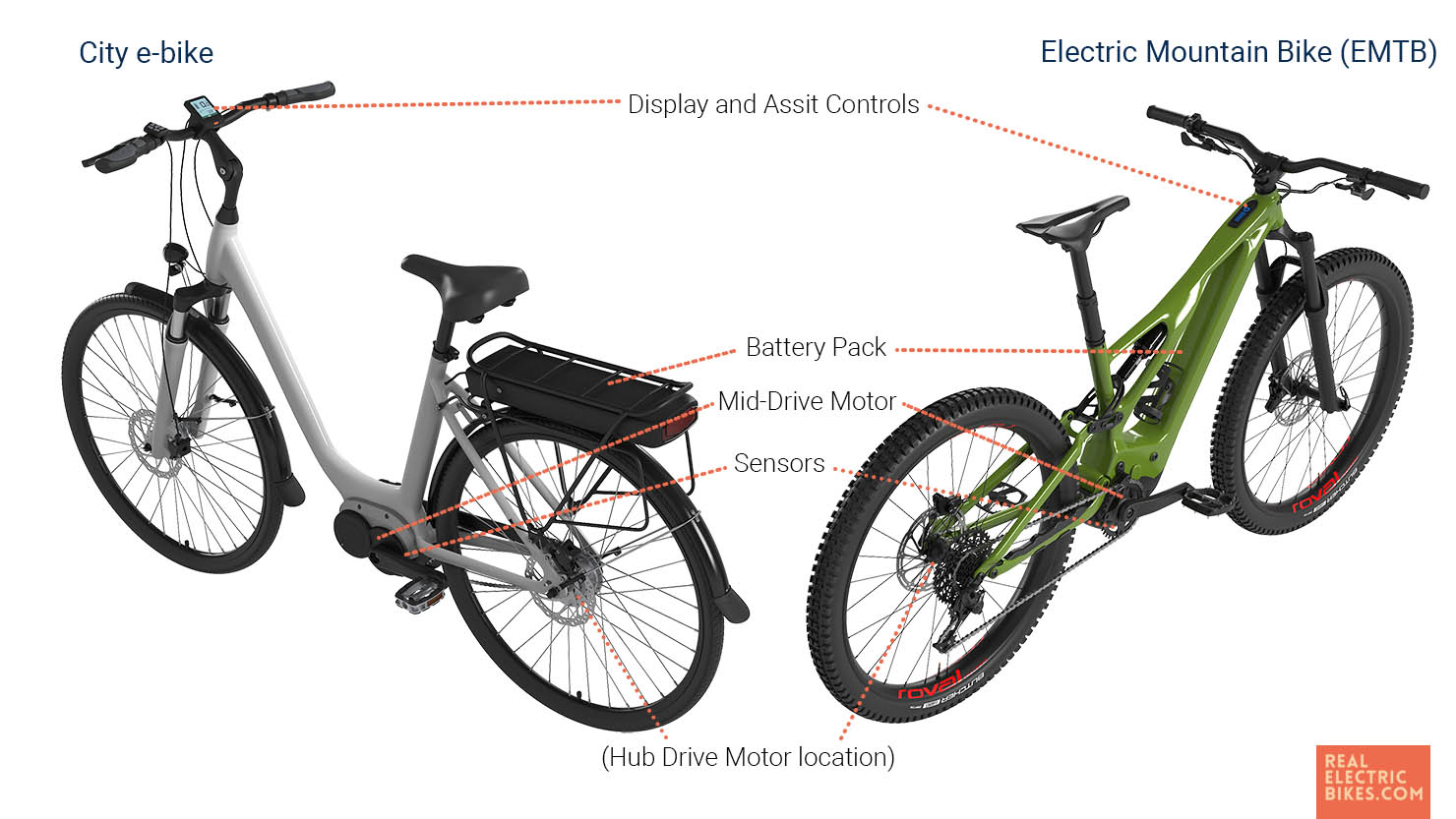
An electric bike (e-bike) is like a normal pedal bike. It has all the components you are familiar with, such as a frame, seat, brakes, levers, wheels, pedals, and handlebar.
But an electric bike is more advanced with electronic and technological solutions.
In addition, an e-bike has a battery, some buttons, sensors, and an electric motor to assist you. They sense when you are pedaling and give you a boost to make it easier to ride.
If you can ride a traditional bicycle, switching to an electric one is easy without needing new skills.
You can adjust the level of boost with different levels of assist. Usually between three or five levels. The more assist you receive, the more battery you will use.
If you want less help during an exercise, you turn the assist down to a low setting.

If you are concerned about speed, remember that you will only get boosted up to 20 or 28 mph, depending on the bike type. If you want to go faster, you must pedal yourself.
We call e-bikes that assist only when you pedal “pedelec,” short for Pedal Electric Bike. In our experience, these are the most popular bikes since they are legal everywhere.
Some electric bikes have a throttle that will assist you even when you are not pedaling. These belong to their a class of bikes and are illegal in some areas.
The motor is usually placed at the axle of the front or rear wheel, called a hub drive.
If the motor is center mounted in the frame at the crank, they are called a mid-drive motor.
Cheaper bikes often have hub-drive motors in the rear or front because they are easy to attach and install with the wheel.
Mid-drive motors, on the other hand, often rely on the frame design and are a little bit more complicated. Electric mountain bikes often feature them because they are well suited for off-road and hilly areas.
Batteries are mounted on the frame, either on the down tube or under the rear rack. Lightweight batteries can also be stored inside the frame in more expensive bikes.
The battery is made of lithium-ion cells, which are common in a lot of electronic equipment. Inside a typical battery, there are around 50 smaller batteries with a resemblance to AA batteries.
A battery management system controls them, or BMS for short, which is an electronic circuit board inside the battery.
Normal batteries are made to last from 500 to 800 charge cycles but usually last much longer.
External batteries are usually removed for charging indoors. Some bikes with built-in batteries are directly connected to the charger.
Charging a battery takes 2 to 8 hours, depending on its size, the charger’s power, and the brand.
You can ride electric bikes with the assist turned off completely or even if the battery is dead.
More about watt-hours and battery capacities further down.
There are two types of sensors. The bike will either have a torque sensor or a cadence sensor. Torque sensors regulate the assist power by how hard you push the pedals. Cadence sensors sense how fast you are pedaling.
The best bikes use torque sensors, while cheaper bikes have cadence. Some bikes have both.
Check out our glossary if you need an explanation of difficult words and abbreviations.

Why are e-bikes so popular?
E-bikes are probably the fastest-growing new means of transport on the planet. Many countries view them as a viable alternative to a car. This is especially true in urban environments. Experts estimate that e-bike sales worldwide will reach 100 million in 2035.
A survey shows that people feel safer on e-bikes than on traditional bikes. The electric assist allows them to avoid dangerous roads. It also allows them to cross intersections and match traffic speed quickly. This enhances their safety. [1]
Riding an e-bike in the city reduces pollution. It saves road space and eases the strain on public facilities. They have low running costs, and parking is easy and free.
The carbon footprint of an electric bike is much lower than that of cars and even electric cars.
The beauty of an e-bike is that it offers all the versatility and advantages of a traditional bicycle. They are easy to use, you don’t need a license, and you don’t need to pay tax or insurance.
An e-bike increases the range you can travel.
It lets you explore parts of the city where cars can’t go. It also takes you to distant trails you wouldn’t visit otherwise.
The motor helps with going up hills without tiring you out. But you will still get the health benefits of bicycling. That is a huge plus.
You can usually wear your normal clothes rather than training clothes. There is no need for changing and showering.
We experience that riding an e-bike makes us happy and gives us a good conscience. It can also help seniors and people with disabilities to get out more.
We think e-bikes are the true future of transportation.
What types of e-bikes are there?

E-bikes are offered in a variety of types and styles. This includes electric cargo bikes, city bikes, mountain bikes, folding bikes, road bikes, cruisers, and more. Some even have tree wheels, which are called e-trikes.
They all have different capabilities and benefits, and the price range varies greatly.
The most common style is probably the city bike. It offers a bit of everything. It’s easy to ride, with a down tube that makes getting on and off simple. It has a rear rack for carrying things, mounts for panniers, mudguards, and lights, and is affordable.
Another popular bike is the e-cargo bike. They often come with double batteries for longer range. The price can be a bit higher, but they can easily replace a car for many of the day-to-day tasks.
Long Tail versions come with a bench seat in the back that can be used by either a couple of kids or a grown-up passenger. Panniers on the side can hold a whole week of groceries and shopping bags.
The other common design is a Long John, where the load area is in the front of the rider over the front wheel. You will find a wide variety of designs. For instance, some are more suited for transporting a couple of kids to school.
Electric mountain bikes, or EMTBs, are increasingly popular amongst mountain bikers. The main advantage is that you can go further and steeper without getting tired.
Nowadays, you even get road bikes with concealed batteries in the down tube and motors in the rear hub. Often, it is almost impossible to see that the bike has electrical components. The only giveaway is a button on the top tube that controls the motor.
These road bikes can be expensive and are more for enthusiasts.
What are the three classes of e-bikes?
Electric bikes are divided into classes. You should know about these three classes of e-bikes that are sold in US stores.
You don’t need a license or insurance if you choose an e-bike in classes one to three.
- Class 1 – Pedal assistance only up to 20 mph (32 km/h). No throttle. A pedelec.
- Class 2 – Pedal assistance and throttle up to 20 mph.
- Class 3 – Pedal assist only up to 28 mph (45 km/h). Usually no throttle.
Remember that you can always pedal electric bikes faster than the motor helps you.
How much extra weight in an e-bike?
Electric bikes weigh more than normal bikes because of added components. But it is not a problem since the components help you push the extra weight.
The electrical components will typically add 10-20 pounds (4.5 – 9kg) to the bike’s weight.
On expensive road bikes, the motor and battery may only add an extra weight of 7 pounds (3.5kg).
New motor and battery technology are developing all the time. Hence, the weight goes down, and the range increases.
Most e-bikes have a walk mode to help you push the bike around. This is especially useful when pushing up stairs or steep ramps.
What is the best e-bike motor?
In our experience, we see that all motors work. As mentioned, the most affordable bikes usually have hub-drive motors because they don’t require a special frame design.
Hub-drive motors usually get information from a sensor on the crank, which can cause a slight delay. They sense if the pedals are turning or not.
Also, they can add a little bit more work if you have a puncture and need to remove the wheel.
A mid-drive motor is usually best for several reasons. They are usually better at producing power at low speeds, are more efficient, work best on hilly landscapes, and are better for the bike’s balance.
Since they are directly connected to the crank, they are much better at sensing and instantly adding the power you need. These motors usually use a torque sensor that detects how much effort you put into the pedaling and adds power accordingly.
So, a mid-drive motor is smoother, and a hub-drive motor is a bit more on and off and doesn’t feel that natural.
Bosch and Shimano motors dominate the mid-drive market. Bafang and Mahle are also two good hub-drive brands. Other good brands are Yamaha, Specialized, FSA, and Fazua.
Understanding the e-bike battery capacity
Dont stop reading if this looks difficult. Its really not.
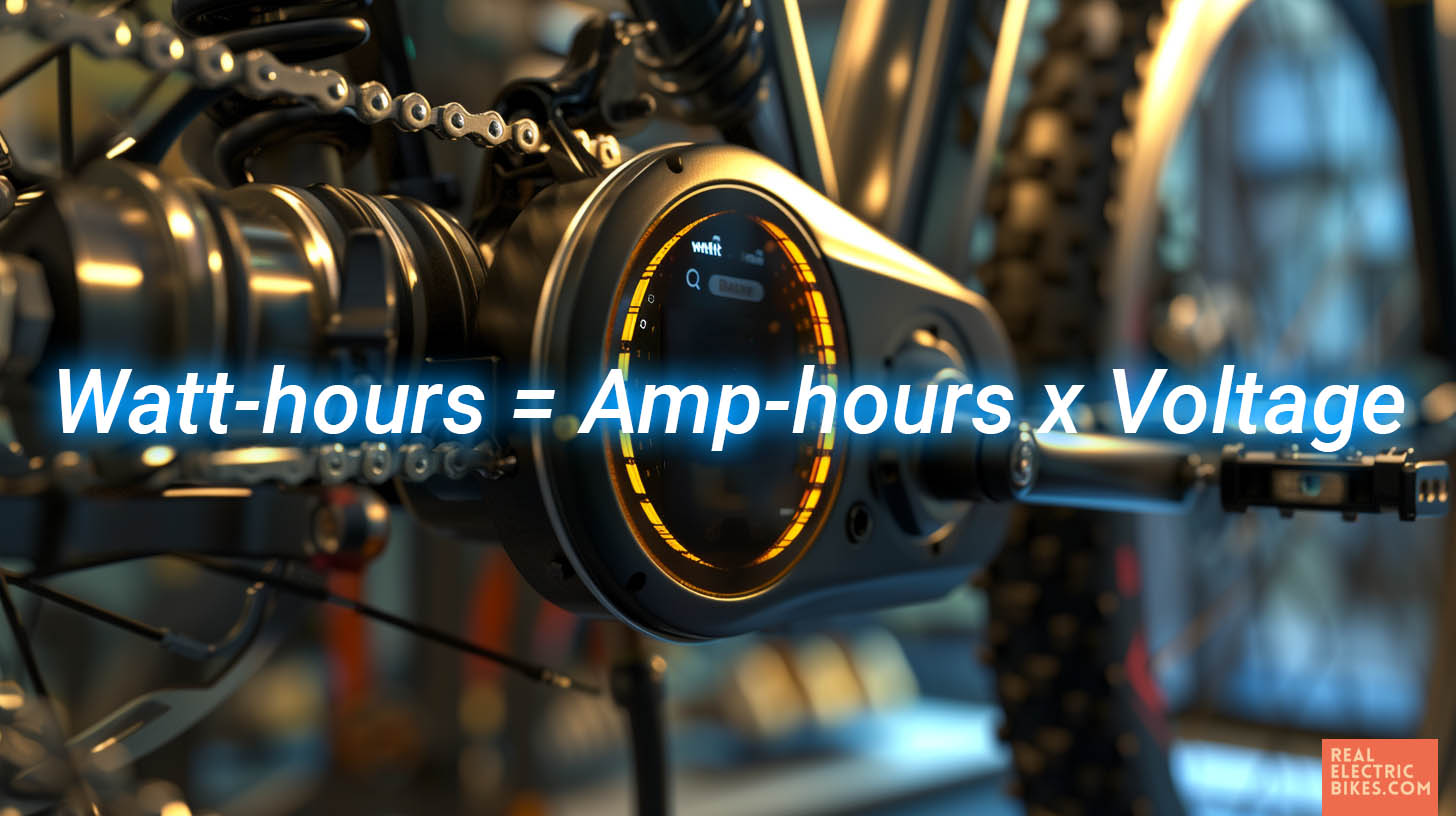
Electric bikes have various battery capacities, measured in watt-hours (Wh). It tells you about the potential energy storage capacity of the battery and how many watts can be delivered in an hour.
More watt-hours mean an increased range.
You might find amp-hours (Ah) mentioned, but watt-hours are better for comparing all bikes, regardless of their voltage system.
You can easily calculate between the systems. Just multiply the amp capacity with the voltage to get watt-hours.
Watt-hours = Amp-hours × Voltage
For instance, it is a 10Ah battery on a 36V system, 360 watt-hours. (10 x 36 = 360).
On everyday riding without too many hills, one mile will cost around 20 watt-hours.
Light and cheap city bikes may have low-capacity batteries of around 250 Wh.
Most e-bikes have medium-capacity batteries ranging from 250 Wh to 500 Wh. It strikes the balance between weight, cost, and range.
E-bikes designed for longer rides and heavy-duty use often come with a capacity of 750 Wh and more.
The range you get from a single charge changes based on many factors. The battery size, the bike’s weight, the terrain type, the rider’s weight, how much pedal assist you use, the battery’s age, and the weather all count.
Usually, a 500 Wh battery can last about 30-70 miles per charge, but it can change a lot.
Sony, Samsung, and Panasonic are reputable battery manufacturers with good batteries.
What to do next?
Now you understand the basics of what an e-bike is. Check out other articles or guides to learn more about electric bikes. We recommend a more detailed article about how electric bike works.


